Blockchain

Public

Private

Consortium

Hybrid
What is Blockchain?
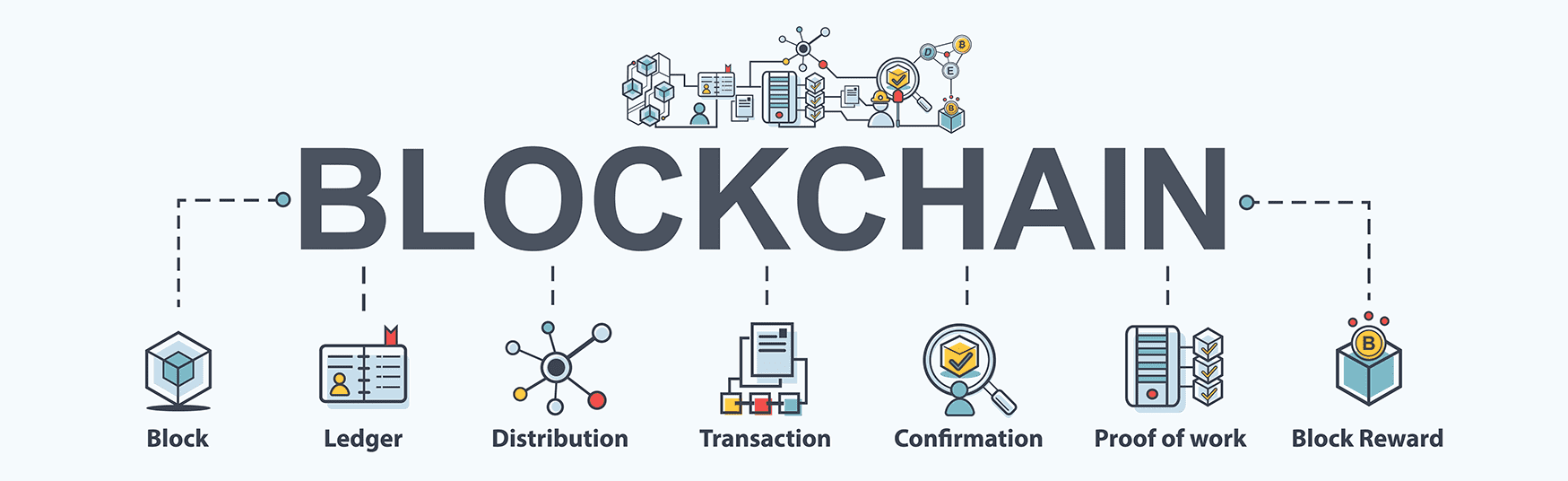
Think of Blockchain as a system that can record your information and make it difficult or near impossible to change, hack or cheat. A digital registry of duplicated transactions is conveyed through the entire network of computer systems on the chain. Each block will contain a number of transactions or actions, and when a new one occurs, it is added to each participant’s transactions history within the chain.
The advantages of this are endless. It is easy to see if one part of the chain is ever tampered with or hacked. The system is programmable, incredibly secure, permanent, time-stamped, and distributed anonymously across all parties. Implementing these systems can be an incredible asset for your business, but it requires some evaluation to see if it makes sense.
The History Of Blockchain
Blockchain is very young in the tech space and started in 1991 with Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta envisioning blockchain technology with their first work on a cryptographically secured chain of blocks.
For 17 years, blockchain stayed quiet, but in 2008, the first blockchain was made by Satoshi Nakamoto. In the year to follow, he released the first paper about the technology in 2009, which outlined its benefits, such as how it would enhance digital trust considering how decentralized it was. He quickly passed this on to other developers, specifically in the Bitcoin development area, and blockchain technology had its start and its future laid out in front of it.
Types Of Blockchain
Public
These blockchains have no permissions, which means anyone can join, and they are entirely decentralized. Public blockchains allow all to have equal rights and access to the chain to create new blocks of data and validate them.
Private
These blockchains require permission to access them and are controlled by a single company. In this chain, the central authority determines who can participate and what capacity they have in the chain, such as who can create new blocks, who can validate them, and who can join.
Consortium
This is another type of permission blockchain where a group of organizations govern it. The advantage of this is that with more governing bodies, the more decentralized it is, leading to high security levels. Once again, to participate, a user requires permission from the consortium in some way.
Hybrid
Hybrids are a combination of the public with the control of the private. They are controlled by a single organization, but there is oversight of the public blockchain, which is required for certain transaction validations within the chain.
How Does Blockchain Help My Business?
Blockchain benefits start externally with greater transparency of information amongst partners and effortless traceability. Internally, the value of increased efficiency with no middlemen in many processes and the value of the security it brings to your initiatives. Each of your transactions is encrypted and linked to the previous, saving you from any chance of falsified information.
How Can LT3 ATG Implement Blockchain?
Blockchain has to make sense for your business from a logistics perspective, which can be difficult to determine. At LT3 ATG, we specialize in finding where blockchain can fit into your business model. Then promptly create your unique chain, adding security, transparency, and efficiency every step of the way. So book your consultation, and let’s get started today!
Blockchain
Related Services
Related Articles
No related articles at the moment
Related Projects
Check out our other projects →LT3 ATG
Ready to get started?
Building your vision starts with a conversation. We're always happy to chat.